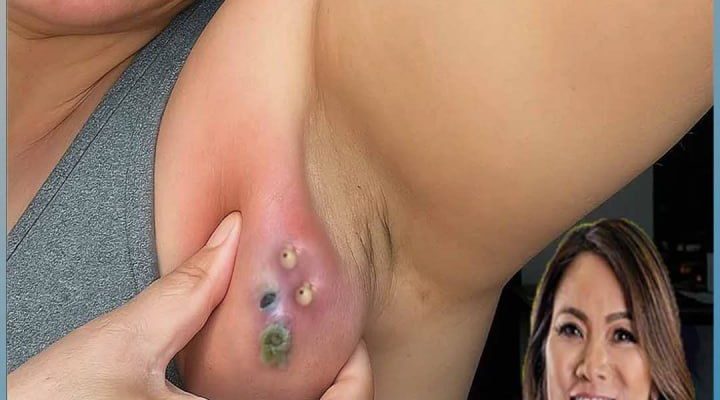
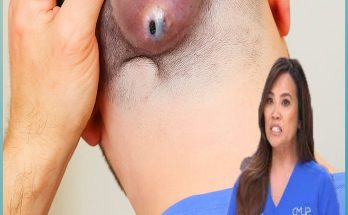
An abscess under the arm, often called an axillary abscess, is a localized infection that occurs when bacteria invade hair follicles, sweat glands, or small cuts in the skin. This leads to the accumulation of pus, swelling, and redness, creating a painful lump beneath the surface of the skin. While such abscesses can appear in anyone, they are particularly common in individuals who sweat excessively, shave frequently, or have weakened immune systems.
Causes of Underarm Abscesses
Underarm abscesses usually develop due to a bacterial infection, most commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus. This bacterium lives harmlessly on the skin but can cause infection when it enters deeper layers through broken skin or irritated hair follicles. Some of the leading causes include:
-
Poor Hygiene: Accumulation of sweat, bacteria, and dead skin cells can lead to clogged pores and infections.
-
Friction and Shaving: Shaving the underarms can create micro-tears that allow bacteria to enter.
-
Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A chronic skin condition that leads to recurrent boils and abscesses in sweat gland–bearing areas.
-
Ingrown Hairs: When hair grows back into the skin, it can cause irritation and infection.
-
Weakened Immune System: People with diabetes, HIV, or those on immunosuppressant medication are more prone to infections.
Symptoms of an Underarm Abscess
The symptoms of an underarm abscess can vary depending on its severity but commonly include:
-
Swelling and redness in the affected area
-
A warm, painful lump that may be tender to touch
-
Pus or fluid-filled lesions that may rupture and drain
-
Fever or chills in severe infections
-
Dark discoloration or necrotic (blackish) areas if the infection becomes advanced
As seen in the image, multiple small pus-filled spots, redness, and swelling indicate a severe form of infection that needs immediate medical attention.
Possible Complications
If left untreated, an abscess can worsen and spread the infection to surrounding tissues, leading to a condition called cellulitis. In more severe cases, the infection can spread to the bloodstream, causing sepsis, a life-threatening condition. In chronic cases, repeated abscesses may leave behind scars or sinus tracts that make future infections more likely.
Treatment Options
1. Medical Drainage
For large abscesses, a healthcare professional may need to perform an incision and drainage procedure. This involves making a small cut in the abscess to release the pus, followed by cleaning and dressing the wound.
2. Antibiotic Therapy
Doctors may prescribe antibiotics to treat the underlying bacterial infection, especially if there are signs of spreading infection or fever.
3. Warm Compresses
Applying a warm compress several times a day can help increase blood flow to the area and promote natural drainage.
4. Pain Relief
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
5. Good Hygiene Practices
Keeping the underarm area clean and dry helps prevent further infection. Avoid shaving until the infection has healed completely.
Home Care and Prevention Tips
-
Clean the underarm area daily with mild soap and water.
-
Avoid sharing razors, towels, or deodorants with others.
-
Use an antibacterial wash if prone to recurrent boils.
-
Wear loose, breathable clothing to prevent sweat buildup.
-
Maintain a balanced diet and manage chronic health conditions that can lower immunity.
When to See a Doctor
You should seek immediate medical attention if:
-
The swelling is rapidly increasing in size.
-
There is severe pain, redness, or black discoloration.
-
You develop a fever or chills.
-
The abscess does not drain or heal within a week.
-
The infection recurs frequently in the same area.
Conclusion
An underarm abscess may start as a minor irritation but can quickly develop into a serious infection if ignored. Prompt treatment, proper hygiene, and medical guidance are key to preventing complications. Whether caused by shaving, ingrown hairs, or underlying health conditions, early care can ensure faster recovery and healthier skin.